Learning objectives
- Compare and contrast how NAD+ is regenerated in respiration and fermentation
- Compare and contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic metabolic pathways in terms of pathway locations, terminal electron acceptors, and responses to absence of oxygen
- Predict how metabolic pathways respond to the absence of terminal electron acceptors
- Differentiate between fermentation and anaerobic respiration
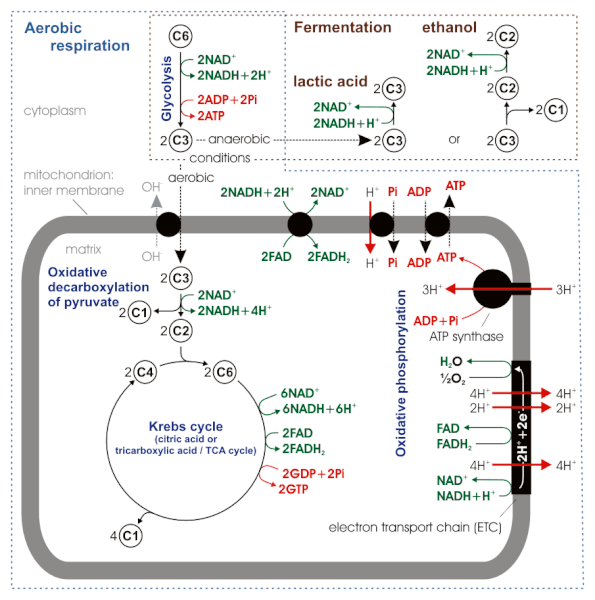
NAD+ is regenerated differently in respiration versus fermentation
Some cells make ATP solely via substrate-level phosphorylation, either because they lack the electron transport chain or because suitable terminal electrons acceptors are unavailable. They use glycolysis to make 2 ATP and 2 pyruvates from a molecule of glucose while generating 2 NADH. However, such cells cannot continue running glycolysis indefinitely because they quickly run out of NAD+ when all available NAD+ has been reduced to NADH. In respiring cells, NADH dumps electrons to the electron transport chain and regenerates NAD+. In the absence of respiration, this method of regenerating NAD+ is not available, but fermentation can produce NAD+. Fermentation is the process by which organic carbon acts as an electron acceptor. Fermentation regenerates NAD+ in the absence of an electron transport chain.
Fermentation reactions reduce pyruvate with electrons from NADH to regenerate NAD+ (opposite of pyruvate oxidation). These reactions produce ethanol in yeast and lactic acid in mammalian cells, specifically in muscle cells under oxygen deficit and in most tumor cells (see Warburg effect below).


Fermentation reactions occur in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate does not enter the mitochondria in eukaryotic cells.
Energy metabolism in eukaryotes vs prokaryotes
In prokaryotic cells, all the metabolic pathways occur in the cytoplasm, except for chemiosmosis and oxidative phosphorylation, which occur on the plasma membrane. Prokaryotic cells are capable of anaerobic respiration using alternative electron acceptors such as nitrate and sulfate, although they prefer oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor to drive chemiosmotic ATP synthesis. In the absence of any suitable electron acceptor, they use fermentation pathways.
In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis and fermentation reactions occur in the cytoplasm. The remaining pathways, starting with pyruvate oxidation, occur in the mitochondria. Most eukaryotic mitochondria can use only oxygen as the terminal electron acceptor for respiration. In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate enters the mitochondrial matrix and is oxidized to acetyl-CoA, and then to CO2 via the citric acid cycle. The electron transport chain and ATP synthase are located on the mitochondrial inner membrane. In the absence of oxygen, pyruvate does not enter mitochondria, but instead undergoes fermentation to either lactic acid or ethanol.
The video below reviews what happens when cells cannot respire to create ATP:
Incorporate this new information into the endosymbiotic theory for origin of mitochondria
We read earlier about the endosymbiotic theory of the origin of eukaryotes. Now that we know about electron transport, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric acid cycle, the location of the electron transport chain on the inner mitochondrial membrane makes sense in light of the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of mitochondria. These locations correspond to the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of the aerobic bacterial endosymbiont that was the ancestor of mitochondria. The outer mitochondrial membrane derived from the endosomal membrane that originally engulfed the endosymbiont.
Application: Cancer and lactic acid fermentation
In the early 1900s, the Nobel Prize winner Otto Warburg observed that many if not most cancer cells derive most of their energy from glycolysis and lactic acid fermentation, even when oxygen is plentiful (Liberti and Locasale, 2016). Several explanations have been proposed. One is that cancer cells can promote biosynthesis and cell growth by not respiring organic carbon to CO2. The organic carbon is instead used to build cellular biomolecules. Another hypothesis is that ramping up glycolysis allows tumor cells to out-compete normal cells or immune system cells for glucose. A third hypothesis is that lactic acid secretion causes changes in the environment of the tumor cells that favors tumor cell growth and spread.
References
Liberti MV, Locasale JW (2016) The Warburg Effect: How Does It Benefit Cancer Cells? Trends Biochem Sci 41:211 – 218 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2015.12.001
A couple of music videos for your study breaks:
Sustainable Development Goal

UN Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure – Fermentation allows for ATP generation when oxygen is not available. This is important in anaerobic environments, such as the bottom of lakes and ponds, where organisms such as bacteria and yeast survive by carrying out fermentation. Studying such organisms has lead to insights on the factors that promote fermentation as a metabolic process, as well as the factors that preserve ecosystem health through the utilization of different metabolic pathways under specific conditions. Providing organisms with the conditions that favor fermentation, or selectively remove the ability to ferment, also has industrial applications in the production of bread, beer, and wine. Here, toggling the ability of organisms to ferment creates characteristic molecules (like flavors and alcohols) and preserves food safety by limiting the growth of disease-causing microorganisms.


A good, brief summary of respiration in eukaryotes in this Biology Crash Course video on ATP and respiration by Hank Green: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=00jbG_cfGuQ
I have a question on the formation of lactate. When I compare the two lactate molecules with the 2 pyruvates, there are 4 additional H atoms. So, does each NADH lose 2 Hydrogen atoms, or is there another source of H atoms?
The additional H atoms are protons picked up from dissociation of water. Water spontaneously dissociates into H+ and OH- ions; at neutral pH (pH 7), the concentration of H+ is 10exp-7 Molar. The complete equation for reduction of pyruvate is: pyruvate + NADH + H+ –> lactate + NAD+
CNN has a story about a couple who learned that their child has a mitochondrial disease: http://www.cnn.com/2012/09/21/health/mitochondrial-disease-martin-family/index.html